How AI Is Transforming Music Streaming Services
The evolution of the music industry is happening in a blink of an eye. The catalyst of all this is, of course, the Internet. Even though vinyl and CDs are a trend again, streaming platforms still generate the largest part of the music industry’s revenue.
Today, artificial intelligence is taking over the music streaming industry and becoming one of its main pillars. From analyzing the listeners’ tastes and preferences to coming up with spot-on recommendations, AI is one of the top driving factors of these services. As a result, all major streaming companies continue to invest more and more in AI to enhance user experience and stay ahead of the competition.
We are going to look at the three largest streaming services by the number of paying users – Spotify, Apple Music, and Amazon Music. Let’s take a look at how each of these companies utilizes AI to provide more value to its listeners.
Spotify: The Streaming Giant
Spotify is currently the largest streaming service by the number of active paying subscribers. Many of its users choose this platform because of its exceptionally unique AI tools for music recommendations. The insurmountable personalization level attracts many people to use Spotify, and it all started with clever acquisitions.
Back in 2017, Spotify bought a couple of companies working with machine learning and data science. Among them was Niland, a French AI startup, which classifies as a music search and recommendation engine provider. With the help of these companies – especially Niland – Spotify came up with one of its signature components – Discover Weekly.
Music lovers receive a constantly updated playlist called “Discover Weekly” with tracks that Spotify thinks may interest them every Monday. The playlist comprises about 50 songs, which are all new to the user. AI tools scan the listener’s preferences and find similar-sounding tracks to offer. But it’s not as simple as that.
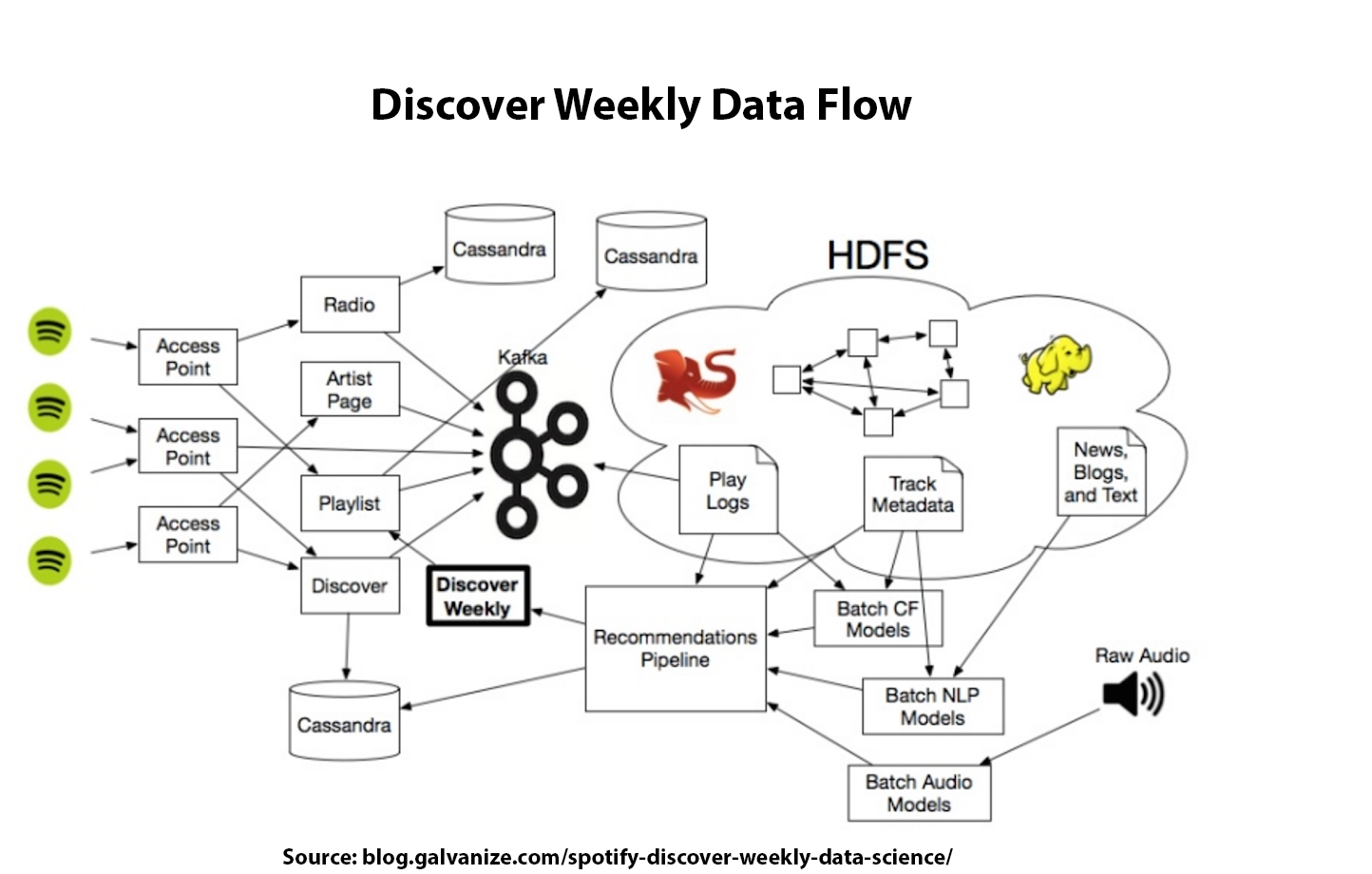
In order to power Discover Weekly, Spotify uses three main models:
- Collaborative Filtering
- Natural Language Processing
- Audio Modeling / Convolutional Neural Networks
Here’s a summary of what the journey looks like.
Collaborative Filtering
With this model, Spotify turns to the listening habits of other users. This algorithm first looks at other user-created playlists that include the same tracks that the given listener plays. It then goes on to see what other songs other users included in the same playlists and filters out common ones to suggest to the listener.
Matrix math by Python libraries is responsible for performing this framework. First, it creates a single matrix with all users and songs. Then it runs different factorization formulas to create two vectors of the song profiles and the taste of a single listener. Finally, the model compares and finds the most similar vectors and gives the collection of recommended songs as an output.
Collaborative filtering is a common method of recommendations employed by multiple companies and industries. Netflix and Amazon use similar models to search through other people’s ratings for suggestions.
While Spotify does not offer ratings for songs, it includes things like the number of plays and number of clicks to the artist’s page from a track in its models to shape valuable recommendations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is a tool in machine learning that interprets human speech via text. The model takes the metadata of a song and scans it through thousands of articles and blog posts about the song and the performer in multiple languages. It can also link the given artist to other artists if there are any mentions in the text.
After the scanning process, the model assigns keywords to artists and tracks, which are then given weights. These are placed into “top terms” and “cultural vectors” categories. The assigned weights are identified based on the relevancy to a particular song or an artist.
For example, if the NLP revolves around ABBA, the top three keywords could be “dancing queen,” “mamma mia,” and “disco era.” Keywords can change their weights day by day. So if you play a random song by ABBA, “Dancing Queen” may pop up in your recommendations when you enter the app later.
Audio Modeling: Convolutional Neural Networks
Because of the lesser popularity of songs not appearing on the radio that often, audio models help these songs end up in people’s libraries too. So, for example, if there’s a new song on the platform by an unknown artist, the NLP model may not take it into consideration, as it pays attention to popularity. The audio model, on the contrary, will not miss out on these tracks if they are potentially something that you would like.
Spotify also implements the convolutional neural networks model for audio, mainly used for face recognition by other companies. The CNN model coils the audio files into different waveforms, which are then assigned separate variables, such as beats per minute, major/minor key, loudness, baseline, and whatnot.
So as you can see, there is a broad spectrum of different components, and Spotify makes sure to utilize all opportunities to deliver the right music to its listeners.
Apple Music: Standing Strong at Number Two
In the rivalry between Apple Music and Spotify, it is difficult to identify a clear-cut winner. After acquiring Siri in 2010, and then Shazam in 2018, Apple made clear that its AI tools are known all over the world.
When it comes to Apple Music itself, the streaming service offers the AI-powered Genius Playlist. The playlist is created when a user likes or adds a single song to his library. The app then scans through the entire catalog of previously played playlists, liked and disliked songs, and skips. In the end, it collects pieces that it considers to be in the same vibe and puts them in an instant playlist, which the listener can find under Genius Playlist on the main page.
During the first days of quarantine back in 2020, Apple Music took to cheering people up and introduced its new AI-driven Get Up! Mix Playlist. The playlist is constantly updated with up-tempo songs meant to encourage good energy and make people happier. The playlist is available on the “Listen Now” page and is customized for each listener individually.
Amazon Music: Voice Recognition Technology Meets Music Streaming
Amazon Music is the third most popular streaming service, and it’s not hard to understand why when looking at its AI tools. Millions of people have recently acquired a new best friend named Alexa in their houses (some have even fallen in love with her, no kidding). In reality, Alexa (or Amazon Echo) is Amazon’s unique voice recognition technology that makes playing music unbelievably effort-free.
When a song only sticks in your head for one line and you can’t recall the artist or the song’s name, it can be quite annoying. With Alexa, you can just say: “Hey Alexa, play: you don’t have to be rich to be my girl,” and it will play “Kiss” by Prince.
The machine learning tool that is Alexa works by keyword spotting. So, Alexa can play whatever song you request as it spots some wake words in your speech and sends them to Amazon’s cloud. Once the cloud verifies the wake words, the request is sent back to you. And all of this happens in a fraction of a second.
Bottom Line
As you can see, you cannot escape AI if you stream your music with any of the major providers out there. These companies have engraved AI in their day-to-day operations and continue to add value to their products.
What does the future of streaming music look like? We can’t say for sure. Twenty years ago, no one would have known that they could find a song by singing a single lyric. One thing we know for sure – the future of music and streaming services is definitely somewhere deeper in the world of machine learning and artificial intelligence.



